
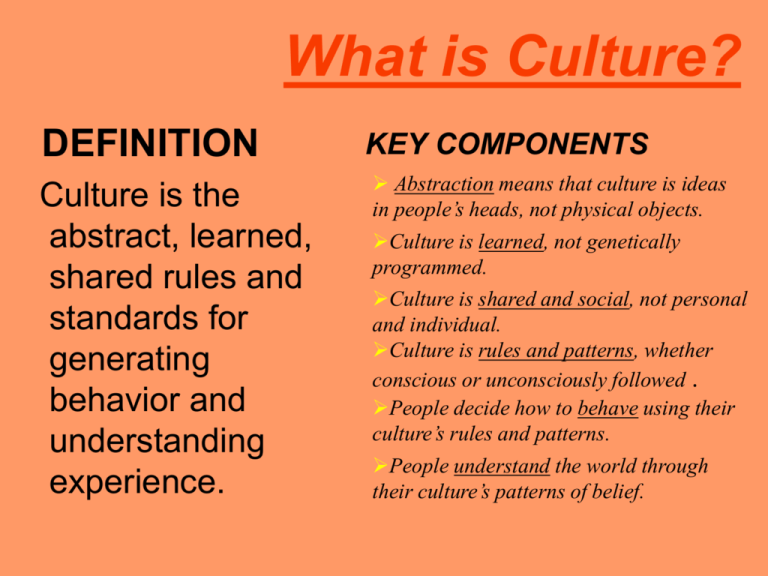
When the terms culture and society first acquired their current meanings, most people in the world worked and lived in small groups in the same locale. A culture consists of the “objects” of a society, whereas a society consists of the people who share a common culture. In time, a large variety of human cultures arose around the world.Ĭulture and society are intricately related. For example, people living in arctic climates developed different cultures from those living in desert cultures.

The term society can also have a geographic meaning and refer to people who share a common culture in a particular location. The cultural bond may be ethnic or racial, based on gender, or due to shared beliefs, values, and activities. Sociologists define society as the people who interact in such a way as to share a common culture. Remember that sociologists define culture differently than they do cultured, high culture, low culture, and popular culture. Low culture, or popular culture-generally pursued by the working and middle classes-refers to sports, movies, television sitcoms and soaps, and rock music. Members of the upper class can pursue high art because they have cultural capital, which means the professional credentials, education, knowledge, and verbal and social skills necessary to attain the “property, power, and prestige” to “get ahead” socially. High culture-generally pursued by the upper class-refers to classical music, theater, fine arts, and other sophisticated pursuits. Popularly speaking, being cultured means being well‐educated, knowledgeable of the arts, stylish, and well‐mannered. Common institutions are the family, education, religion, work, and health care. This latter term institution refers to clusters of rules and cultural meanings associated with specific social activities. Thus, culture includes many societal aspects: language, customs, values, norms, mores, rules, tools, technologies, products, organizations, and institutions. Through culture, people and groups define themselves, conform to society's shared values, and contribute to society.


Sociological Research: Designs, Methods.Complementary Perspectives in Sociology.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
